Featured Paper of the Month – August 2022
Published in The Journal of Neuroscience by Hong-Ju Yang, Briana J Hempel, and Zheng-Xiong Xi, et al. of the NIDA IRP Addiction Biology Unit.
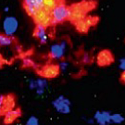
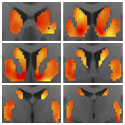
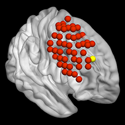
It is well known that glutamate plays an important role in relapse to drug seeking. However, the role of glutamate in drug reward is unclear. In this report, we found that elevating extracellular glutamate level in the nucleus accumbens (NAc) by TFB-TBOA, a selective astrocyte glutamate transporter inhibitor, dose-dependently inhibits cocaine self-administration and brain-stimulation reward. Mechanistic assays indicate that prolonged cocaine self-administration selectively upregulates NMDA-GluN2B receptor subtype expression in striatal dopaminoceptive neurons…